Classification of RP rapid prototyping technology
Classification of RP rapid prototyping technology
Rapid prototyping (RP) is an innovative technology that can directly produce complex parts in a matter of hours using 3D CAD designed graphics. Specifically, it is divided into laser rapid prototyping (SLA), lamination rapid prototyping (LOM), powder sintering rapid prototyping (SLS), melt deposition rapid prototyping (FDM) and 3D printing technologies. Since the advent of the first rapid prototyping system in 1988, more than two dozen systems have been developed, each with some minor differences. Initially, these systems were used in the automotive and aviation fields, and later in many other fields, such as toys, computers, jewelry and medicine.
Stereoscopic light curing (SLA) : SLA method is the first commercialized RP technology with the largest market share. It takes photosensitive resin as raw material, computer-controlled ultraviolet laser scans the surface of the photosensitive resin point by point according to the cross-section information of each layer of the part, so that the thin layer of the resin in the scanned area produces photopolymerization reaction and curing, forming a thin layer of the part. After a layer is cured, the workbench is moved down a layer thick distance to apply a new layer of liquid resin on the surface of the original cured resin, and then the scanning processing of the next layer can be carried out. The newly cured layer sticks firmly to the previous layer, and so on until the entire prototype is built.
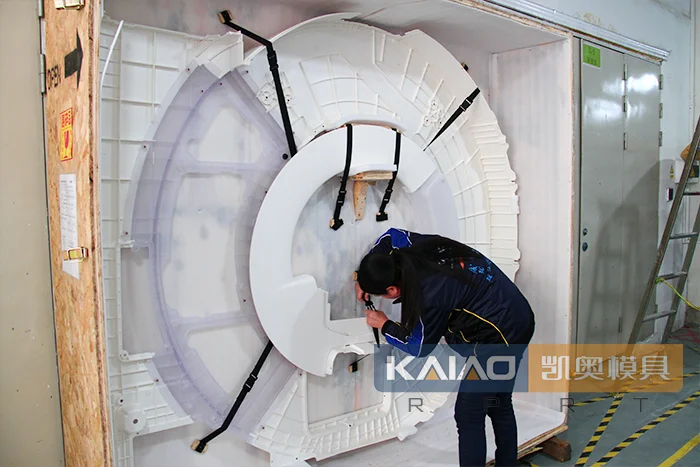

Fused deposition (FDM) : The FDM method was invented in 1988. The molten material sprayed in the nozzle is driven by the X-Y workbench, and is spread on the bottom plate according to the cross-section shape, and processed layer by layer, and finally the part is manufactured. Commercial FDM equipment uses a wide range of materials, such as cast paraffin, nylon, thermoplastics, ABS, etc. In addition, multiple nozzles can be used to improve efficiency.
Laser selective sintering method (SLS) : The SLS method uses infrared lasers as energy sources, and the modeling materials used are mostly powder materials. During processing, the powder is first preheated to a temperature slightly lower than its melting point, and then the powder is paved under the action of a scraping stick; The laser beam is selectively sintered according to the stratified cross-section information under computer control, and then the next layer is sintered after the completion of a layer, and the excess powder is removed after the completion of all sintering, then a sintered part can be obtained. At present, the mature process materials are wax powder and plastic powder, and the sintering process with metal powder or ceramic powder is still under research.
Laminated method (LOM) : The LOM method was introduced in 1985. First of all, lay a layer of foil (such as paper) on the substrate, and then use a certain power of infrared laser under the control of the computer to cut out the outline according to the stratification information, while the non-parts are cut into pieces according to a certain grid shape for removal, after processing a layer, then lay a layer of foil, rolled by hot rollers, so that the newly laid layer is stuck on the formed body under the action of adhesive. The shape of the layer is cut again, and so on until the processing is complete. ** Remove the chopped excess, you can get a complete part.

3D printing technology: 3D printing technology is functionally the same as laser forming technology (SLA), using layered processing and superimposed forming, that is, by adding materials layer by layer to generate 3D entities, the printing process of each layer is divided into two steps, first spray a layer of special glue in the area that needs to be formed, the glue droplet itself is small and not easy to spread. Then a uniform layer of powder is sprayed, and the powder will quickly solidify and bond when it encounters the glue, while the area without glue remains loose. In this way, under the alternations of a layer of glue and a layer of powder, the solid model will be "printed" molding, and after printing, as long as the loose powder can be "planed" out of the model, and the remaining powder can be recycled.
In China, the main use of laser rapid prototyping technology (SLA), Kaiao company introduced 3D SYSTEM 250 series of rapid prototyping machine, processing accuracy up to ±0.05mm, affordable processing cycle is generally 3~4 days, welcome to the picture consultation!